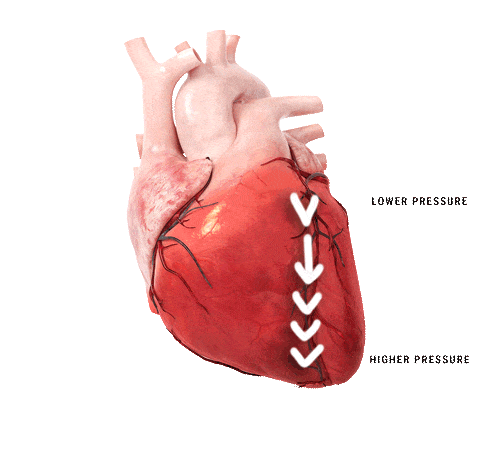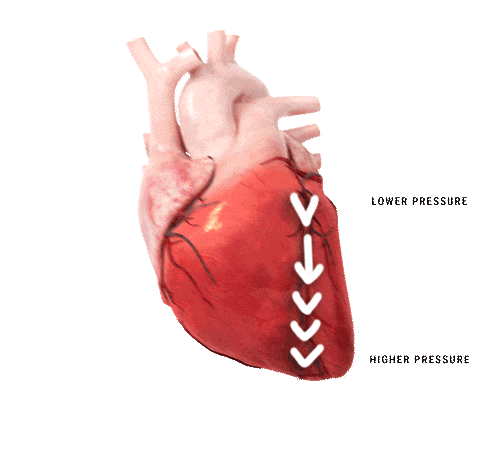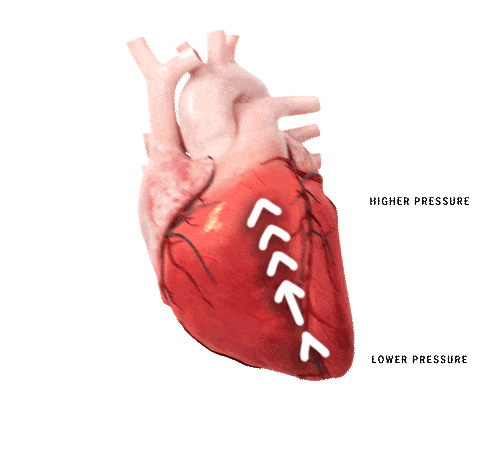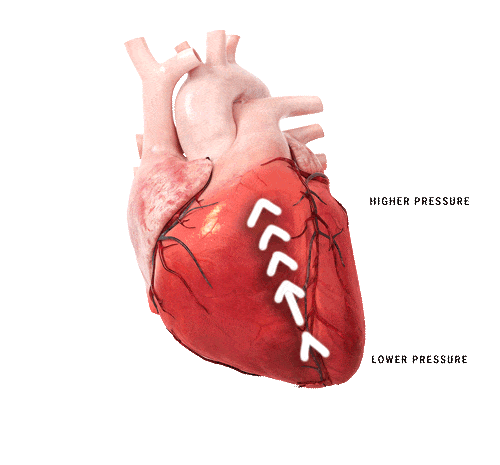
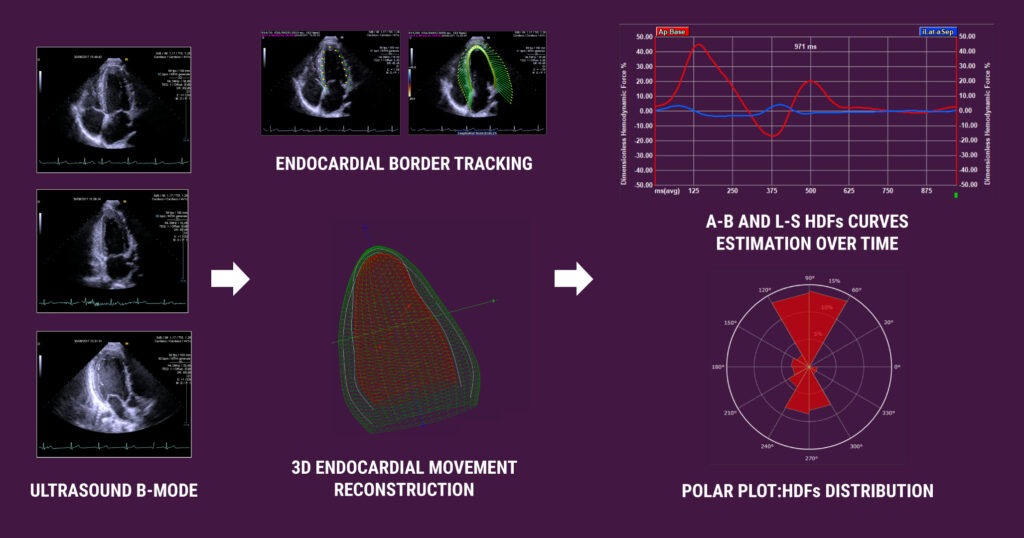
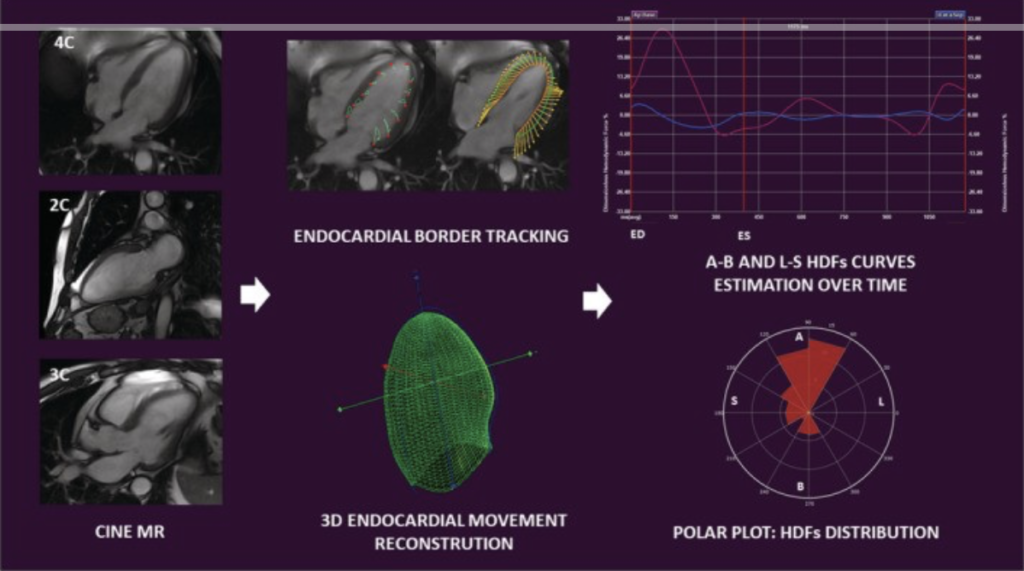
Heart failure
Diagnosis
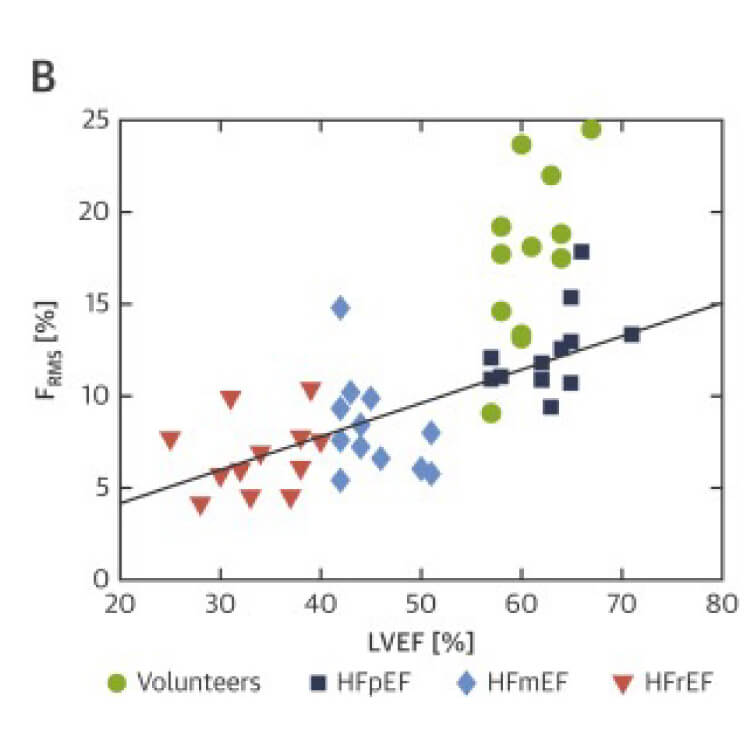
In case of heart failure with either mid-range or reduced ejection fraction (resp HFmEF and HFrEF) values of strain and ejection fraction can help with the diagnosis. However, those values can’t distinguish healthy volunteers and patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) making early diagnosis challenging. The new HDF parameter shows promising results with a study by Lapinskas et al that indicates HDF may significantly improve the detection of early systolic dysfunction [5].
Treatment
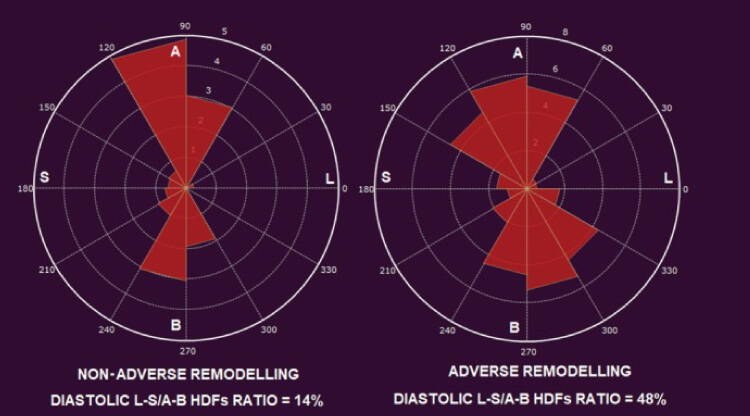
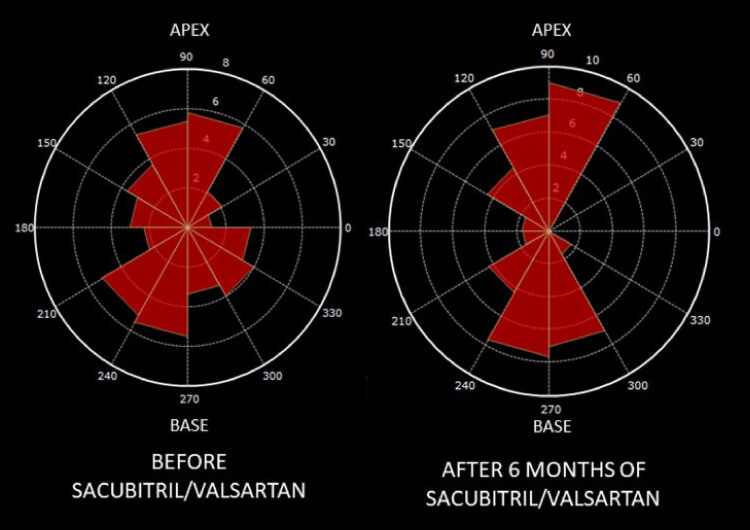
In case a patient is diagnosed with heart failure and medication therapy is prescribed, a follow-up on the evaluation of the cardiac remodeling is needed. It has been shown that for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) the HDF can be used as follow-up methodology. Patients treated with sacubitril/valsartan therapy showed re-alignment of the HDF after 6 months, indicating reverse remodeling of the LV [6].
For symptomatic heart failure patients without response on medical therapy, cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) is an established strategy. However, despite efforts to identify the appropriate candidates for CRT the response of the therapy is heterogeneous. Research shows that pacing-induced realignment of HDFs is associated with CRT efficacy at follow-up which might help with the patient selection [7].