Dr. J Westra and multiple co-authors, under the supervision of Dr. EH Christiansen, Dept of Cardiology, Aarhus University Hospital in Denmark, published this interesting paper in JACC Imaging.
Read MoreDr. Lee KY from the Department of Cardiology, Incheon St. Mary’s Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, and co-authors from other Korean universities published in Nature Scientific Reports a comprehensive study involving 915 patients with angina and acute myocardial infarction (AMI), where QFR demonstrated high diagnostic accuracy, exceeding 95% for identifying fractional flow ratio (FFR) ≤ 0.8 in the angina group and 92% in the AMI group.
Read MoreWe are happy to announce that we will host another Medis QFR® Academy session, this session will feature Prof. Eric Van Belle, esteemed Head of Interventional Cardiology at University Hospital of Lille, France. He will guide us through the intricacies of using QFR in the context of ST-elevated myocardial infarction (STEMI). This session will illuminate the pivotal role of QFR in distinguishing between culprit and non-culprit lesions, using two detailed clinical case studies as a backdrop for discussion. This session will be moderated by Dr. Ignacio J Amat Santos From University of Valladolid Medical Centre in Spain.
Read MoreIn the field of coronary revascularization, where identifying reversible myocardial ischemia is paramount, FFR and iFR are standard but underutilized due to various limitations. QFR, an angiography-derived method, emerges as a potential game-changer, providing functional assessment without additional wires or hyperemic agents and showcasing a shorter measurement time than invasive methods. In conclusion, the study, aligning with ongoing trials, suggests that a QFR-guided strategy could simplify, enhance safety, and cost-effectively guide revascularization decisions. Furthermore, the findings position QFR as a promising tool to boost the adoption of physiology-based revascularization in routine clinical practice.
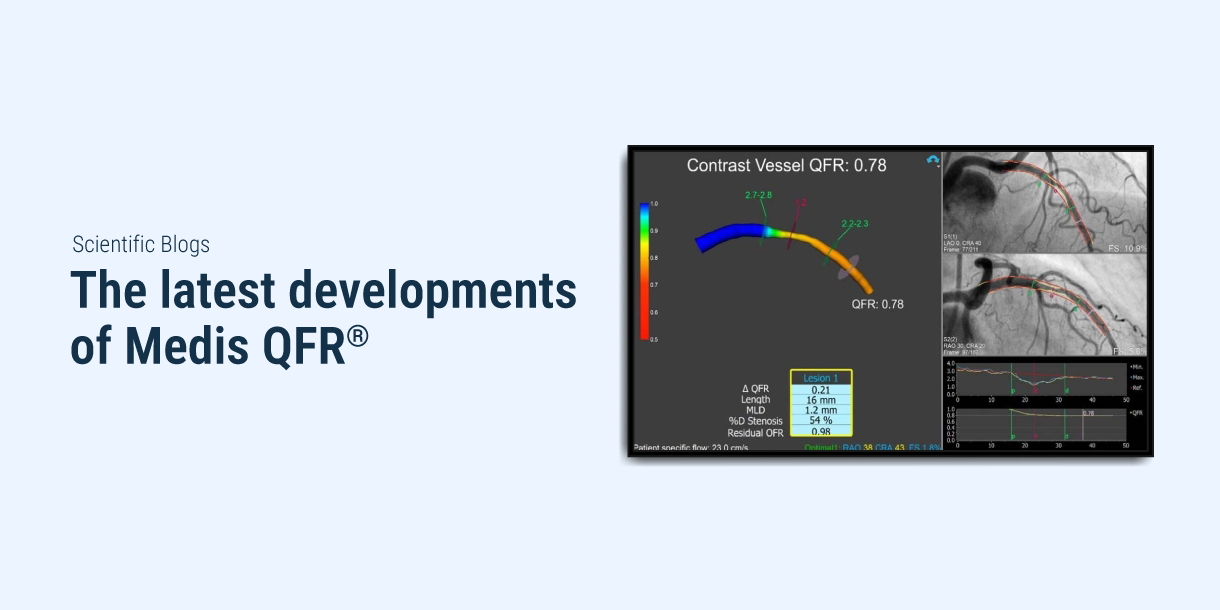
Read MoreIn this march edition of the Medis QFR® blog article we are proud to share five publications with you.
Read MoreIn this february edition of the Medis QFR® blog article we are proud to share five publications with you.
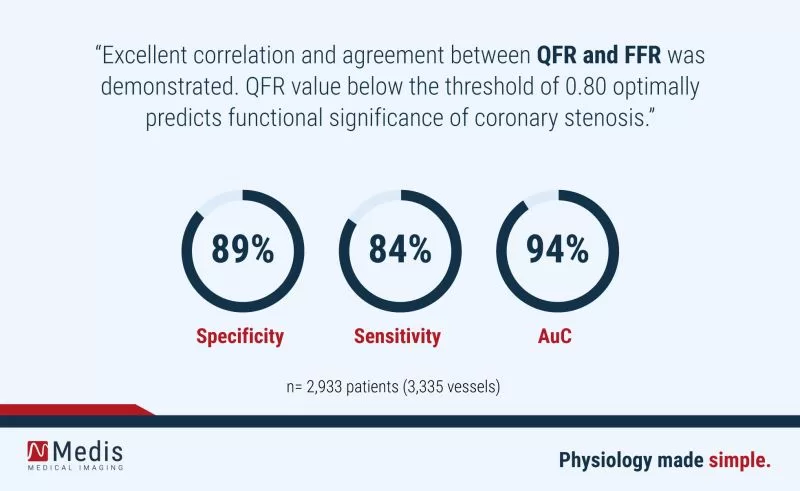
Read MoreCortés C. et al. published in Catheter Cardiovascular Interventions Journal an interesting meta-analysis and systematic review on QFR.
Read More